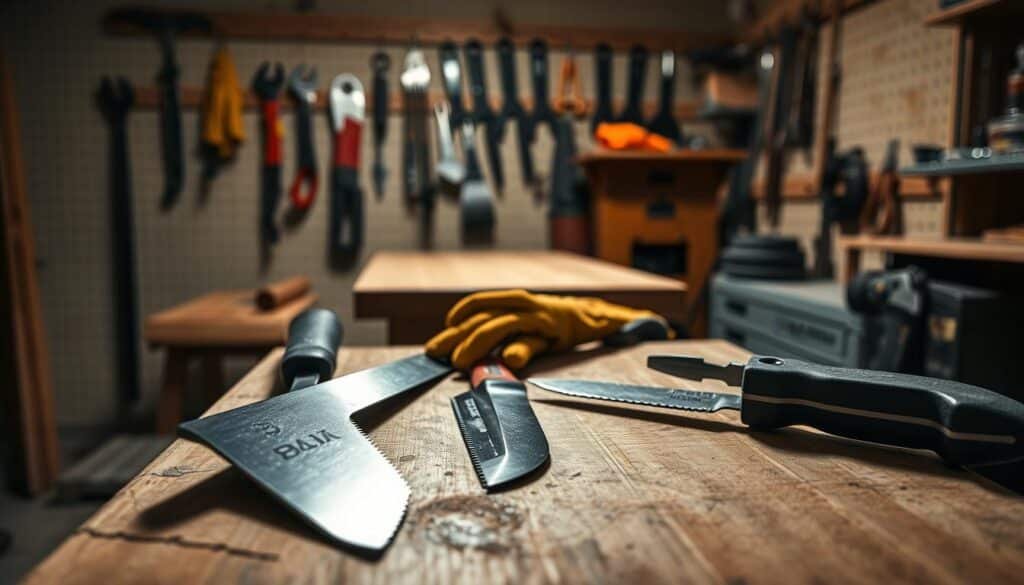
Working with sharp tools can be dangerous if not done right. One wrong move can cause serious harm, making a DIY project into a trip to the hospital.

It’s key to know the right ways to use knives, chisels, and saws safely. This is important for anyone who works with tools, whether you’re a hobbyist or a pro.
Using the right safe tool handling methods helps avoid big mistakes. It also keeps your workshop safe.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the importance of safe tool handling practices.
- Learn proper techniques for handling knives, chisels, and saws.
- Discover how to maintain a safe workshop environment.
- Recognize the risks associated with improper tool handling.
- Adopt safety precautions to prevent injuries.
The Critical Importance of Safe Tool Handling
Learning about safe tool handling is key to a safer DIY journey. It’s not just about keeping yourself safe. It also helps avoid expensive mistakes and ensures your projects succeed.
Preventing Costly Mistakes and Injuries
Safe tool handling is vital to prevent injuries. These can be anything from small cuts to serious lacerations or even losing a limb. Accidents can also cause project delays and extra costs. By using tools safely, DIY fans can dodge these problems.
Statistics on Tool-Related Accidents
Many DIY enthusiasts don’t know how common tool-related accidents are. The United States Consumer Product Safety Commission reports thousands of emergency room visits each year. The table below shows some shocking numbers.
| Type of Injury | Estimated Annual Incidents |
|---|---|
| Lacerations | 12,000 |
| Finger amputations | 3,000 |
| Eye injuries | 2,000 |
Long-Term Benefits of Developing Safe Habits
Creating safe habits with sharp tools offers lasting benefits. It lowers injury risk, boosts project success, and makes DIY work more fun. By focusing on safety, you gain confidence and can take on bigger projects.
Essential Safety Gear for Sharp Tool Work
It’s important to have the right safety gear for sharp tool work. Working with sharp tools can be dangerous without the right precautions. The right safety equipment protects you and makes you feel more confident while working.
Cut-Resistant Gloves and Hand Protection
Cut-resistant gloves are a must for sharp tool work. They protect your hands from cuts and lacerations. Look for gloves made from Kevlar or Dyneema for the best protection without losing dexterity.
When choosing cut-resistant gloves, consider:
- How well they resist cuts (ASTM or EN standards)
- How comfortable they are to wear for a long time
- How well they let you move your hands
Eye and Face Protection
Eye and face protection is also key. Safety goggles or glasses with a wrap-around design protect your eyes from debris. A face shield is a good idea when using power tools or dealing with lots of debris.
When choosing eye and face protection, look for:
- How well they can handle fast-moving particles
- How clear they are so you can see well
- How comfortable they are to wear
Appropriate Workshop Clothing
Wearing the right workshop clothing helps prevent injuries. Stay away from loose clothes that could get caught in tools. Choose clothes that are tough and won’t cut easily. Wearing long sleeves and pants helps protect against cuts and scrapes.
Tool-Specific Safety Equipment
Each tool needs its own tool-specific safety equipment. For saws, use protective sleeves to avoid kickback injuries. For knives, a cut-resistant apron adds extra protection.
Some examples of tool-specific safety gear include:
- Protective sleeves for saws
- Cut-resistant aprons for knife work
- Dust masks or respirators for tasks that make dust or debris
Knife Safety: Mastering Proper Techniques
Learning knife safety is key for everyone, whether you’re a pro or a DIY fan. It helps avoid accidents in the workshop. By handling knives safely, you ensure both the task and tool are treated with care.
Correct Grip and Hand Positioning
A good grip is essential for knife safety. Hold the knife firmly but not too hard. Place the blade in your dominant hand, with fingers curled under and out of the way.
Your thumb should be on the knife’s spine or handle, not on the blade. Proper hand positioning means keeping your non-dominant hand away from the blade. Use a claw-like grip to guide the material you’re cutting.

Safe Cutting Directions and Body Stance
Always cut the knife away from your body. This lowers the chance of cutting yourself. Stand with your feet apart and face the work area for balance.
Position your body so you’re not leaning over the cutting area. Keep your center of gravity stable.
Storage and Transportation Safety
Knives should be kept in a designated spot, like a knife block or magnetic strip. This prevents them from getting lost or knocked off. When moving knives, use a protective sheath or wrap them up to hide the blade.
Specialty Knife Considerations
Utility knives and folding knives need special care. Make sure the utility knife’s blade is locked before use. Be careful when opening and closing folding knives to avoid pinching or cutting your fingers.
| Knife Type | Safety Consideration |
|---|---|
| Utility Knife | Ensure blade is locked in place |
| Folding Knife | Be cautious when opening/closing |
| Fixed Blade Knife | Use proper sheath when not in use |
By learning these knife safety tips, you can greatly lower injury risks in the workshop. Safety becomes a habit with practice and focus on proper techniques.
Chisel Techniques for Injury Prevention
Chisel safety is key, and knowing the right techniques can lower accident risks. When using chisels, it’s important to know the dangers and how to avoid them.
Preventing Dangerous Kickback
Kickback happens when a chisel kicks back towards you, leading to serious injuries. To stop kickback, make sure your chisel is sharp and use the right method. A dull chisel needs more force, which raises kickback chances.
- Hold the chisel with a firm, but not overly tight, grip.
- Keep your hands and body positioned to avoid being in the direct line of possible kickback.
- Use a mallet or hammer to strike the chisel, instead of applying manual force.
Minimizing Splintering Hazards
Splintering happens when the chisel tears the wood instead of cutting it cleanly. To lessen this risk, cut in the direction of the wood grain whenever you can. Also, a sharp chisel edge reduces splintering.
Proper Workpiece Securing
Securing your workpiece is key to safe chisel use. Use clamps or a vise to keep the workpiece steady, so it won’t move while chiseling. This keeps you in control and lowers accident risks.
Force Control and Body Positioning
Keeping control over the chisel’s force is essential. Stand with a stable stance and keep your body balanced. When hitting the chisel with a mallet, aim for controlled, precise strikes.
By learning these chisel techniques, you can greatly improve your safety in the workshop. Safety is a continuous effort that needs focus and a dedication to following best practices.
Safe Handling of DIY Sharp Tools: Saw Edition
Saw safety is more than just avoiding injuries. It’s also about making precise cuts and keeping control in your projects. Knowing the safety tips for each saw type is key.

Starting Cuts Safely
First, make sure your workpiece is steady. Use clamps or hold it firmly. Start with a slow, controlled push, then apply more pressure if needed. For power saws, align the blade right and set the depth correctly.
- Check the saw blade for damage or wear before use.
- Position yourself to maintain balance and control.
- Use a push stick or other safety device when necessary.
Maintaining Control Throughout the Cut
Keeping control is vital for safe saw use. Keep your hands and fingers away from the blade. Use both hands to guide the saw, if you can. For circular saws, keep the base flat against the workpiece to avoid kickback.
Key tips for maintaining control include:
- Keeping a firm grip on the saw.
- Moving the saw at a steady, consistent pace.
- Avoiding overreaching or stretching while cutting.
Different Saw Types and Their Specific Safety Needs
Each saw has its own safety needs. Handsaws need careful handling to avoid cuts. Circular saws require attention to kickback prevention. Coping saws, with thin blades, need precise control to avoid breakage and injury.
Finishing Cuts Without Injury
When finishing a cut, watch out for the saw’s momentum and the risk of the blade binding or kicking back. For power saws, let the blade stop completely before setting the saw down.
Always inspect your workpiece after cutting to ensure it meets your project’s requirements and that no damage occurred during the cut.
Creating a Workshop Environment for Accident Prevention
The layout and conditions of your workshop are key to preventing accidents. A well-designed workshop boosts productivity and lowers injury risks.
Optimal Lighting and Visibility
Good lighting is vital for a safe workshop. Bad lighting can cause accidents because it makes it hard to see. Make sure your workshop is bright, with focused lighting for detailed work. LED lights are great for their brightness and energy use.

Proper Tool Storage Systems
A tidy workspace is safer. A good tool storage system keeps things organized and tools easy to find. This saves time and prevents accidents from misplaced tools. Use toolboxes, pegboards, and wall storage.
Non-Slip Surfaces and Stability
Slip, trip, and fall accidents are common. To avoid these, keep your floor clean and clutter-free. Use non-slip mats or coatings in areas where you stand a lot or tools are moved often.
Organizing for Safety and Efficiency
Organizing your workshop for safety and efficiency is more than just tool storage. It’s about arranging your space to reduce movement and improve visibility. Place often-used tools and materials where they’re easy to reach. Make sure your workbench is at a comfortable height to avoid strain.
By focusing on these areas, you can make your workshop safe and efficient. This reduces accident risks and improves your DIY projects.
Common Mistakes That Lead to Tool Injuries
It’s important to know the common mistakes that cause tool injuries. These mistakes can lead to accidents. By understanding and fixing these errors, we can stay safe at work.
Rushing and Distraction Dangers
Rushing and being distracted are big risks for tool injuries. When you rush, you might apply too much pressure or lose control. Distractions can also make you forget what you’re doing, leading to accidents. It’s key to stay focused and calm when using tools.
The Hazards of Dull Tools
Dull tools are as dangerous as sharp ones used wrong. They need more force, which can lead to accidents. Keeping your tools sharp is a good way to avoid these dangers.
Improper Tool Selection
Using the wrong tool can cause injuries. Tools are made for specific tasks. Always pick the right tool for the job to stay safe.
Fatigue and Its Impact on Safety
Fatigue is a big risk for tool injuries. When tired, you react slower and make more mistakes. Make sure to rest well before starting work to avoid accidents.
| Mistake | Consequence | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Rushing cuts | Increased risk of accidents | Take your time, stay focused |
| Dull blade dangers | Loss of control, increased force required | Regularly sharpen tools |
| Improper tool selection | Tool misuse, accidents | Choose the right tool for the job |
| Fatigue mistakes | Impaired judgment, slow reaction times | Take regular breaks, rest when needed |
First-Aid Preparedness for Tool-Related Injuries
A well-stocked first-aid kit is key to handling tool-related injuries. Even with careful work, accidents can occur. Being ready can lessen the impact of injuries.
Essential Workshop First-Aid Kit Components
A basic first-aid kit should have bandages, antiseptic wipes, gloves, and scissors. For a workshop, add specialized items like burn cream, eye wash solution, and tweezers.
| Item | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Bandages | Wound dressing |
| Antiseptic wipes | Wound cleaning |
| Gloves | Protection from infection |
Treating Common Tool Injuries
For minor cuts, clean the wound with antiseptic wipes and cover with a bandage. For deeper cuts or severe bleeding, apply pressure to stop the bleeding.
When to Seek Professional Medical Help
If an injury is serious, or if there’s a chance of tetanus infection, get medical help right away. Look for signs of infection like redness, swelling, and more pain.
Emergency Response Planning
Plan for emergencies by knowing the nearest medical facility and how to quickly call for help.
Teaching Tool Safety to Beginners
Teaching tool safety to beginners is key to a safe work area. It’s important to show new users how to handle tools right. This helps avoid accidents and keeps the workspace safe.
Age-Appropriate Tool Introduction
When teaching kids about tools, start with the right ones for their age. Choose tools that fit their skill level. This lowers the chance of accidents.
Effective Demonstration Techniques
Showing how to use tools is vital. Demonstrate the right way to hold and use tools. Also, stress the need to stay focused on the task.
Supervised Practice Methods
After showing how to use tools, let beginners practice with supervision. An experienced person should guide them. This ensures they use safety techniques correctly.
Building Confidence Safely
As beginners get more experience, help them build confidence safely. Start with simple tools and tasks. Always keep the work area safe.
| Age Group | Tool Introduction | Supervision Level |
|---|---|---|
| 6-10 years | Basic hand tools | High |
| 11-14 years | Simple power tools | Moderate |
| 15+ years | Advanced power tools | Low to Moderate |
By following these steps, you can teach tool safety well. This makes the workplace safer and more confident for everyone.
Conclusion: The DIYer’s Safety Checklist
Keeping your workshop safe is key for DIY fans. By following safe practices and watching out for dangers, you can lower the chance of accidents and injuries.
Having a detailed diy safety checklist is important. It should cover regular tool checks, proper storage, and wearing protective gear. Also, stay alert and avoid distractions when using sharp tools.
For tool safety, learn the right ways to handle knives, chisels, and saws. A safe workshop is organized, well-lit, and has non-slip floors.
DIYers should always put safety first. Regularly check and update your safety checklist to spot and avoid dangers.
What are the most common injuries associated with sharp tool handling?
Common injuries from sharp tools include cuts, lacerations, and puncture wounds. These often happen from bad grip, cutting towards the body, or dull blades.
How can I prevent kickback when using a chisel?
To avoid kickback, secure the workpiece well. Hold the chisel firmly and control the force. Keep your body ready to dodge the chisel if it kicks back.
What safety gear is essential for working with sharp tools?
Key safety gear includes cut-resistant gloves and safety goggles. Also, a workshop apron and tool-specific safety items like finger guards are important.
How should I store sharp tools to prevent accidents?
Store sharp tools in a designated area with blades covered. Keep them out of children’s reach. Use toolboxes or wall storage to keep things organized and safe.
What are the best practices for maintaining control while cutting with a saw?
Start with a steady motion when cutting with a saw. Keep your body positioned to avoid being hit if the saw binds. Use the right saw for the job and keep it sharp.