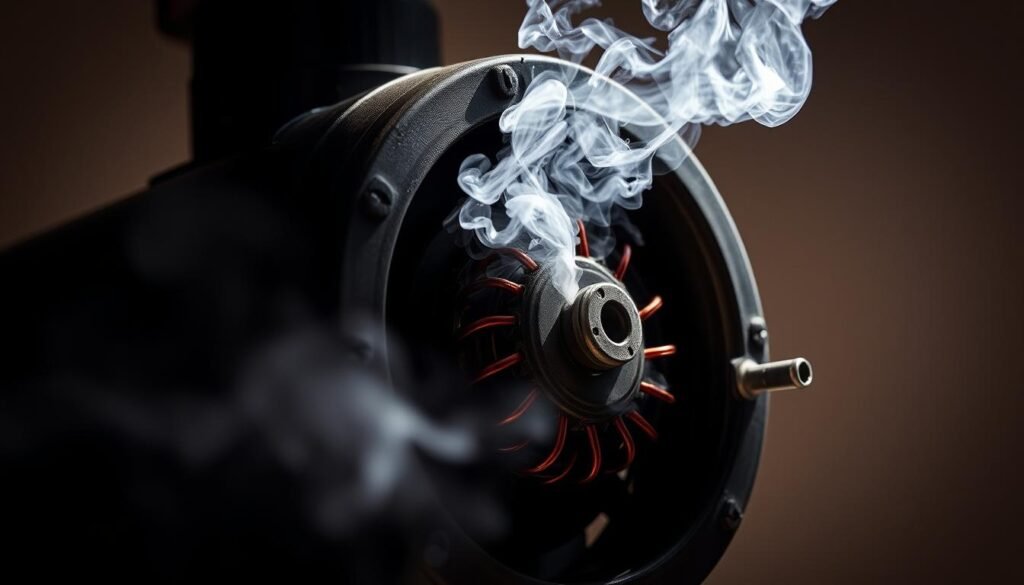
Motor overheating is a common issue that can significantly impact the performance and longevity of power tools. When a motor overheats, it can lead to reduced efficiency, increased wear and tear, and even complete tool failure.
Understanding the causes and signs of overheating is crucial for maintaining tool health and preventing damage. By identifying the root cause of the problem, users can take corrective action to repair or maintain their tools, ensuring optimal performance and extending their lifespan.
Proper diagnosis and timely intervention can save time and money by reducing the need for costly repairs or replacements.
Key Takeaways
- Motor overheating can lead to reduced tool performance and lifespan.
- Understanding the causes and signs of overheating is crucial for tool maintenance.
- Proper diagnosis can help prevent costly repairs or replacements.
- Timely intervention can save time and money.
- Regular maintenance is key to preventing motor overheating.
Why Motor Overheating Matters in Power Tools
Overheating motors in power tools pose significant risks to users and the tools themselves. Motor overheating is a pervasive issue that can lead to serious consequences if not addressed promptly.
Safety Risks of Overheating Tools
One of the most critical concerns with motor overheating is the safety risk it poses. Overheated tools can cause burns, start fires, or lead to electrical shocks. For instance, an overheated motor can melt the internal components, potentially causing a short circuit.
- Risk of burns from touching hot tool surfaces
- Potential for fires due to overheated components
- Electrical shock hazards from damaged insulation
Impact on Tool Performance and Lifespan
Motor overheating not only poses safety risks but also significantly impacts the performance and lifespan of power tools. Excessive heat can degrade the motor’s internal components, leading to reduced efficiency and eventual failure.
- Reduced tool performance due to overheating
- Shortened lifespan of the motor
- Increased maintenance costs over time
Financial Implications of Motor Burnout
The financial implications of motor burnout due to overheating can be substantial. Repair or replacement costs can be significant, not to mention the potential loss of productivity due to tool downtime.
| Cost Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Repair Costs | High |
| Replacement Costs | Very High |
| Productivity Loss | Significant |
By understanding the causes and consequences of motor overheating, users can take proactive steps to mitigate these risks and ensure their power tools operate safely and efficiently.
Recognizing the Warning Signs of an Overheating Power Tool
When using power tools, it’s crucial to be aware of the warning signs that indicate overheating, as ignoring these signs can lead to serious damage or safety hazards. Power tool motor overheating symptoms can manifest in various ways, and being able to identify these signs early on is key to preventing further damage.
Physical Indicators: Heat, Smoke, and Odors
One of the most obvious signs of an overheating power tool is excessive heat emanating from the tool, particularly around the motor or battery area. Users should also be cautious of smoke or burning odors, as these are clear indicators that the tool is overheating. If a tool emits a burning smell or smoke, it should be turned off immediately to prevent further damage.
Performance Issues: Slowing, Stalling, and Power Loss
Overheating can also cause performance issues with power tools. If a tool begins to slow down, stall frequently, or experiences a noticeable loss of power, it may be overheating. These performance issues are often accompanied by increased noise or vibration, signaling that something is amiss.
Unusual Sounds and Vibrations
Unusual sounds, such as grinding or screeching noises, and increased vibrations are other indicators that a power tool may be overheating. These signs suggest that internal components are being overstressed, potentially leading to motor failure if not addressed.
Recognizing these warning signs early can help prevent minor issues from becoming major problems, ensuring that power tools continue to operate safely and efficiently.
Common Causes of Power Tool Motor Overheating
The overheating of power tool motors is a multifaceted issue, influenced by both internal and external factors. Understanding these causes is crucial for preventing damage, ensuring safety, and maintaining tool efficiency.
Electrical Issues and Voltage Problems
Electrical issues are a primary cause of power tool motor overheating. Voltage fluctuations or using the wrong power source can lead to motor strain. For instance, using a power tool with a battery that is not compatible with the tool’s voltage requirements can cause the motor to work harder, generating excessive heat.
- Incompatible voltage supply
- Faulty wiring or connections
- Overloaded circuits
To mitigate these issues, it’s essential to check the tool’s manual for the correct voltage and to ensure that all electrical connections are secure and not damaged.
Mechanical Factors: Friction and Binding
Mechanical factors, such as friction and binding, can also contribute to overheating. When parts within the tool bind or experience excessive friction, it can cause the motor to work harder, leading to increased heat production.
- Lack of lubrication
- Worn or damaged parts
- Misaligned components
Regular maintenance, including lubricating moving parts and replacing worn components, can help reduce the risk of overheating due to mechanical factors.
Environmental Conditions: Dust, Debris, and Temperature
Environmental conditions play a significant role in power tool motor overheating. Dust and debris can clog tool vents and coolings systems, while operating in high-temperature environments can directly contribute to overheating.
- Operating in dusty or debris-filled environments
- High ambient temperatures
- Inadequate tool ventilation
To combat these issues, users should regularly clean their tools and avoid using them in extremely hot conditions whenever possible.
Operational Misuse and Overloading
Operational misuse, including overloading the tool, is another common cause of overheating. Using a power tool beyond its capacity or for extended periods without adequate cooling breaks can lead to excessive heat buildup.
To prevent overheating due to operational misuse, it’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for usage and to take regular breaks to allow the tool to cool down.
Diagnosing Overheating Motors: Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
To prevent damage and ensure optimal functioning, diagnosing the cause of overheating in your power tool is essential. A systematic approach helps in identifying the root cause, whether it’s related to electrical issues, mechanical factors, or environmental conditions.
Visual Inspection Techniques
A visual inspection is the first step in diagnosing an overheating motor. Look for signs of wear, damage, or blockages. Check the tool’s exterior, vents, and cooling systems for dust accumulation or debris.
- Inspect the power cord and plug for any signs of damage.
- Check for loose connections or worn-out parts.
- Ensure that the ventilation system is clear of obstructions.
Testing for Electrical Problems
Electrical issues are a common cause of overheating. Testing the motor’s electrical components can help identify problems.
- Use a multimeter to check for voltage drops or irregularities.
- Inspect the brushes and commutator for wear or damage.
- Check the wiring for any signs of deterioration or damage.
Checking Mechanical Components
Mechanical factors such as friction and binding can cause a motor to overheat. Inspecting these components is crucial.
Key areas to check include:
- The bearings and gears for signs of wear or misalignment.
- The shaft and other moving parts for any binding or excessive friction.
Using Diagnostic Tools Effectively
Diagnostic tools can provide valuable insights into the motor’s condition. Using these tools effectively is key to a successful diagnosis.
Some useful diagnostic tools include:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Multimeter | Measures voltage, current, and resistance. |
| Thermal Imaging Camera | Identifies hotspots and temperature anomalies. |
| Oscilloscope | Analyzes waveforms to detect electrical irregularities. |

By following this step-by-step guide, you can effectively diagnose and address overheating issues in your power tools, ensuring they continue to operate efficiently and safely.
Quick Fixes for Overheating Power Tools
When your power tool overheats, it’s crucial to act quickly to prevent damage and ensure safety. Overheating can lead to reduced tool lifespan, performance issues, and even safety hazards. Fortunately, there are several quick fixes you can apply to address the problem.
Cooling Down an Overheated Tool Safely
The first step in dealing with an overheated power tool is to cool it down safely. Turn off the tool and unplug it from the power source to prevent any accidental start-ups. Allow the tool to cool down naturally; avoid using water or other substances to cool it down quickly, as this can cause damage.
- Place the tool in a well-ventilated area to help it cool down faster.
- Avoid touching hot parts of the tool to prevent burns.
- If the tool has a thermal shutdown feature, let it reset before using it again.
Cleaning Ventilation Systems and Air Intakes
A common cause of overheating is clogged ventilation systems or air intakes. Regular cleaning can prevent overheating and maintain tool performance. Use compressed air or a soft brush to remove dust and debris from the vents and air intakes.
Ensure you follow the manufacturer’s instructions for cleaning and maintenance to avoid damaging the tool.
Addressing Simple Electrical Issues
Sometimes, overheating can be caused by simple electrical issues, such as faulty wiring or worn-out brushes. Inspect the tool’s electrical components for signs of wear or damage. Replacing worn-out parts can resolve overheating issues and prevent future problems.
“Regular maintenance, including checking electrical components, can significantly extend the life of your power tools.” – Tool Maintenance Expert
If you’re unsure about how to inspect or replace electrical components, consult the tool’s manual or contact a professional.
DIY Repairs for Common Overheating Problems
When your power tool overheats, it doesn’t always mean you need to replace it; sometimes, a simple DIY repair can get it back to optimal working condition. By addressing common issues such as worn brushes, faulty switches, and inadequate lubrication, you can restore your tool’s performance and extend its lifespan.
Replacing Worn Brushes and Components
Worn brushes are a common cause of overheating in power tools. Inspecting and replacing these components can significantly improve your tool’s efficiency. To do this, first, ensure your tool is unplugged or the battery is removed. Then, locate the brushes, usually found in the motor housing. Remove the old brushes and inspect the brush holders for any debris or wear. Install new brushes, making sure they fit snugly and are properly seated.

Other components that may need replacement include worn bearings and damaged gears. Regular inspection can help identify these issues before they lead to overheating. When replacing these parts, use manufacturer-recommended components to ensure compatibility and performance.
Fixing Faulty Switches and Wiring
Faulty switches and wiring can cause significant electrical resistance, leading to overheating. To diagnose these issues, start by inspecting the switch for any signs of wear or damage. If the switch is faulty, replace it with a new one that matches the original specifications. For wiring issues, check for any frayed or damaged wires and replace them as necessary.
Ensure all connections are secure and not loose, as loose connections can also cause overheating. Use a multimeter to test for continuity and verify that the wiring is functioning correctly.
Lubricating Moving Parts Properly
Proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction and preventing overheating in power tools. Identify the moving parts that require lubrication, such as gears and bearings. Use a lubricant recommended by the tool’s manufacturer, applying it according to the instructions provided.
| Part | Lubricant Type | Application Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Gears | Gear Oil | Every 50 hours of use |
| Bearings | Bearing Grease | Every 100 hours of use |
| Other Moving Parts | Multi-purpose Lubricant | As needed |
By following these DIY repair tips, you can effectively address common overheating problems in your power tools, ensuring they continue to operate efficiently and safely.
Preventive Maintenance to Avoid Motor Overheating
One of the most effective ways to prevent motor overheating in power tools is through consistent maintenance routines. By taking care of your tools, you can significantly reduce the risk of overheating and prolong their lifespan.
Regular Cleaning and Inspection Routines
Regular cleaning is essential for maintaining your power tools. Dust, debris, and other contaminants can accumulate and block cooling vents, leading to overheating. To prevent this, make it a habit to clean your tools after each use, paying particular attention to the vents and air intakes.
Inspection is also crucial. Check for worn or damaged parts, and replace them as needed. This includes inspecting brushes, bearings, and other moving components. By addressing issues early, you can prevent more significant problems from developing.
Proper Storage and Transport Practices
How you store and transport your power tools can also impact their performance and longevity. Avoid storing tools in humid or extreme temperature environments, as this can cause damage to the motor and other components.
When transporting tools, use protective cases or bags to prevent damage from impacts or vibrations. This can help prevent internal components from becoming misaligned or damaged, reducing the risk of overheating.
Cooling Breaks During Extended Use
During extended use, it’s essential to give your power tools regular breaks to cool down. This is particularly important for tools that are used continuously or in high-demand applications.
Allowing your tools to cool down can help prevent overheating, reducing the risk of motor damage. It’s a simple but effective practice that can make a significant difference in the longevity and performance of your tools.
By incorporating these preventive maintenance practices into your routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of motor overheating in your power tools. Regular cleaning, proper storage, and cooling breaks during extended use are all simple yet effective strategies for maintaining your tools and ensuring they continue to perform optimally.
Differences Between Corded and Cordless Tool Overheating Issues
Corded and cordless power tools have distinct characteristics that influence their susceptibility to overheating. While both types of tools can suffer from overheating, the causes and preventive measures differ significantly.
Battery-Related Overheating in Cordless Tools
Cordless tools rely on batteries, which can be a source of overheating due to factors like high discharge rates, deep discharging, and poor battery maintenance. When a battery is deeply discharged or subjected to high discharge rates, it can generate excessive heat, potentially leading to tool overheating.
To mitigate this, it’s essential to follow proper charging practices and maintain the battery according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Regularly checking the battery’s condition and ensuring that it’s properly seated in the tool can also help prevent overheating issues.

Power Supply Problems in Corded Tools
Corded tools, on the other hand, are directly connected to a power source, and their overheating can often be attributed to power supply issues or electrical faults. Voltage fluctuations, inadequate wiring, or using an extension cord that’s too long or too thin can lead to overheating.
Ensuring that the power supply matches the tool’s requirements and using appropriate cords can mitigate these risks. Regular inspections of the cord and plug for damage or wear are also crucial.
Unique Maintenance Requirements for Each Type
Both corded and cordless tools require regular maintenance to prevent overheating. For cordless tools, this includes proper battery care and ensuring that the tool’s ventilation system is clear of debris. For corded tools, maintaining the cord and plug, as well as ensuring that the tool’s internal components are clean and well-lubricated, is vital.
Understanding these differences and adhering to the recommended maintenance practices can significantly reduce the risk of overheating, thereby prolonging the lifespan of your power tools.
When to Repair vs. Replace an Overheating Power Tool
The decision to repair or replace an overheating power tool hinges on several factors, including cost, tool condition, and warranty status. Making an informed decision requires a thorough assessment of these factors to determine the most cost-effective and practical solution.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Repairs
Conducting a cost-benefit analysis is crucial when deciding whether to repair or replace an overheating power tool. This involves comparing the cost of repairs, including parts and labor, against the cost of purchasing a new tool.
- Assess the cost of replacement parts and labor.
- Compare this cost to the price of a new tool.
- Consider the tool’s age, condition, and remaining lifespan.
If the repair cost exceeds 50% of the tool’s original price, it may be more economical to replace it. Additionally, if the tool is old or has other wear issues, replacement might be the better option.
Signs That Indicate Irreparable Damage
Some signs indicate that a power tool is beyond repair. Recognizing these signs can save time and money by avoiding unnecessary repair attempts.
Key indicators of irreparable damage include:
- Visible damage to critical internal components.
- Repeated overheating issues despite proper maintenance.
- Significant loss of performance or functionality.
If your tool exhibits any of these symptoms, it’s likely time to consider replacement.
Warranty Considerations and Professional Repair Options
Warranty status and professional repair options are vital considerations when deciding whether to repair or replace an overheating power tool.
- Check if your tool is still under warranty, as this can significantly reduce repair costs.
- Consult with professional repair services to assess the tool’s condition and obtain a repair estimate.
- Consider the expertise and warranty offered by professional repair services.
For tools still under warranty, contacting the manufacturer or an authorized service center is recommended. For out-of-warranty tools, weighing the cost of professional repair against replacement is essential.
Conclusion: Keeping Your Power Tools Cool and Functional
Maintaining your power tools is crucial for their longevity and safe operation. By understanding the causes of motor overheating and implementing preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of tool damage and ensure a safer working environment.
To keep your power tools cool and functional, follow power tool safety tips such as regular cleaning, proper storage, and avoiding overloading. Understanding how to prevent tool motor from overheating is key to prolonging tool life and maintaining efficiency.
Safe use of tools to avoid overheating involves being mindful of operational misuse, keeping tools well-maintained, and taking regular cooling breaks during extended use. By adopting these practices, you can minimize the risk of overheating and ensure your power tools remain in good working condition.
How can I prevent my power tool from overheating?
To prevent overheating, ensure proper maintenance, including regular cleaning and inspection routines, proper storage and transport practices, and taking cooling breaks during extended use. Additionally, avoid overloading the tool and use it within the recommended specifications.
What are the common signs of an overheating power tool?
Common signs include excessive heat, smoke, unusual odors, slowing or stalling, power loss, and unusual sounds or vibrations. If you notice any of these signs, stop using the tool immediately to prevent further damage.
What causes power tool motors to overheat?
Overheating can be caused by electrical issues, mechanical factors such as friction and binding, environmental conditions like dust and debris, and operational misuse or overloading. Understanding these causes can help you take preventive measures.
Can I repair an overheating power tool myself?
Yes, some repairs can be done yourself, such as replacing worn brushes and components, fixing faulty switches and wiring, and lubricating moving parts properly. However, complex issues may require professional repair or replacement.
What is the difference between corded and cordless tool overheating issues?
Corded tools are more prone to overheating due to power supply problems, while cordless tools can overheat due to battery-related issues. Understanding these differences is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
When should I replace an overheating power tool instead of repairing it?
If the cost of repairs exceeds the tool’s value, or if the tool shows signs of irreparable damage, it’s best to replace it. Additionally, consider warranty options and professional repair services before making a decision.
How can I cool down an overheated power tool safely?
To cool down an overheated tool, turn it off and let it rest in a well-ventilated area. Avoid using water or other cooling methods that could damage the tool. Once cooled, inspect and address the cause of overheating before resuming use.